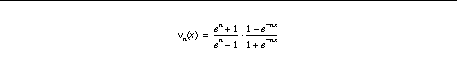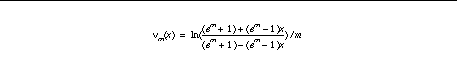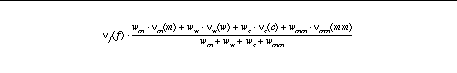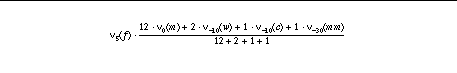The MetaMap Indexing (MMI) methodology consists of:
- Applying MetaMap to text (see MetaMap: Mapping Text to the UMLS Metathesaurus (280 kb)) such as the TItle and ABstract fields of MEDLINE ® citations, and
- Constructing a list of ranked concepts by applying the MMI ranking function to each UMLS® Metathesaurus® concept discovered above by MetaMap.
The rest of these notes consist of a description of the MMI ranking function followed by some examples.
Definition of the ranking function:
Generally speaking, the MMI ranking function was designed to indicate the
characterizing power or
aboutness of a given concept for a piece of text, e.g., a MEDLINE
® citation. It is the product of a
frequency factor and a
relevance factor. The relevance factor is, in turn, a weighted average of four components (listed in order of importance): a MeSH tree depth factor, a word length factor, a character count factor, and a MetaMap score factor. For concepts found in the title of the citation, there is a simplified form of the function which maximizes the frequency factor.
The components of the function:
Before definining ranking function components, themselves, it id worthwhile to point out that each component is
normalized before being combined with other function components. Normalization is accomplished by applying a sigmoidal function to a value. Each sigmoidal function maps from the unit interval [0,1] to itself and is determined by an index. An index of zero determines the identity function (hence, no normalization). A positive index determines a sigmoidal function which lies above the identity and consequently accentuates the differences between small values. Larger indexes produce more accentuation. Conversely a negative index determines a sigmoidal function lying below the identity and consequently accentuates the differences between large values. If we denote the normalization function with index n by nu
n :[0,1]
-> [0,1], then the formal definition of them is:
nu
0 (x) = x;
for n > 0,
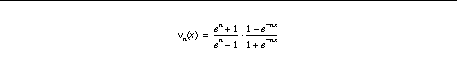
for n < 0 (letting m=-n),
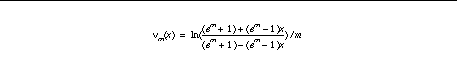
Now the basic ranking function components are defined as follows:
- the frequency, simply denoted f, is the number of times the concept occurs (i.e., is discovered by MetaMap) in the title or abstract fields of the citation divided by 13;
- the MeSH tree depth, m, is the maximum depth of all MeSH tree codes associated with the concept divided by 9. The computation is actually done by counting the number of periods in the tree code;
- the word length, denoted w, is the number of words in the concept divided by 26;
- the character count, denoted c, is the number of characters in the concept divided by 102; and
- the MetaMap score, denoted mm, is just the score divided by 1,000.
Putting it all together:
Using weighting factors denoted by w
m , w
w , w
c, w
mm for MeSH tree depth, word count, character count, and MetaMap score, respectively, the ranking score can be written as:
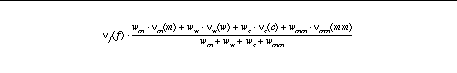
The actual function with weights determined by experimentation is:
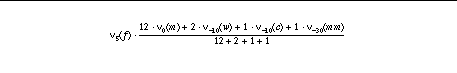
When the concept occurs in the title of the citation, the frequency factor nu
f (f) is replaced by 1. This has the effect of giving title concepts overwhelmingly good rankings.
Ranking examples:
This section contains five examples with 3-point average precisions ranging from superior to the worst possible. Each example consists of the MEDLINE citation and the ranked MMI output. An exclamation mark indicates that the MeSH heading found by MMI occurs in the MH field of the citation; an asterisk indicates a main heading.
The best:
An example with near perfect 3-point average precision of 0.9496.
Citation:
UI - 93121691
AU - Kario K ; Matsuo T ; Nakao K
TI - Cigarette smoking increases the mean platelet volume in elderly
patients with risk factors for atherosclerosis.
AB - To study the effects of cigarette smoking and atherosclerosis on
platelet size, we measured the mean platelet volume (MPV) and other
platelet parameters in 142 elderly smokers and nonsmokers with or
without atherosclerotic risk factors. The MPV and the platelet count
were highest and their inverse correlation was strongest in the
atherosclerotic smokers (r = 0.54, P < 0.05) when compared
with the nonsmoking and non-atherosclerotic groups. A 10% decrease of
MPV was found in 8 smoking subjects in the atherosclerotic group, who
successfully discontinued smoking (P < 0.05). These results suggest
that smoking may increase platelet consumption in atherosclerotic vessels
and that subsequently megakaryocytes are activated to produce larger
platelets, which are more active. Thus, an increase in MPV due to smoking
may also contribute to the acceleration of atherosclerosis and should be
considered as a risk factor for atherosclerotic disease.
MH - Aged ; Aged, 80 and over ; Atherosclerosis/*BLOOD ;
Blood Platelets/ *ULTRASTRUCTURE ; Cell Size ; Comparative Study ;
Female ; Hematopoiesis ; Human ; Male ; Megakaryocytes/CYTOLOGY ;
Platelet Count ; Risk Factors ; Smoking/*BLOOD ;
Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
SO - Clin Lab Haematol 1992;14(4):281-7
PY - 2
MMI concepts for 93121691 (3-pt AP=0.949603):
! 59.5 Risk Factors
! 48.2 *Atherosclerosis
! 34.1 *Blood Platelets
! 33.8 Aged
! 25.8 *Smoking
17.4 Patients
! 9.3 Platelet Count
7.7 Acceleration
! 6.6 Megakaryocytes
5.0 Disease
Good:
An example with good 3-point average precision of 0.8808.
Citation:
UI - 93230262
AU - Bellemare F
TI - Evaluation of human diaphragm function.
AB - When single supramaximal shocks are delivered during relaxation to both
phrenic nerves simultaneously, the resulting transdiaphragmatic pressure
twitch (PdiT) or mouth pressure twitch (PmT) are found to decrease linearly
with increasing lung volume thereby reflecting changes in diaphragm
contractility. Whereas fatigue decreases PdiT at any given lung volume,
chronic lung hyperinflation tends to increase PdiT at any given lung
volume. When the phrenic nerve shocks are delivered during ongoing
voluntary contractions, PdiT decreases with increasing level of diaphragm
activation. Its amplitude thus detects the reverse left for full activation
of the diaphragm by the voluntary motor drive. The ability to maximally
activate the diaphragm decreases with fatigue but is retained in patients
with chronic lung hyperinflation.
MH - Diaphragm/*PHYSIOLOGY; Human ;
Lung Diseases, Obstructive/ PHYSIOPATHOLOGY ;
Muscle Relaxation/PHYSIOLOGY; Phrenic Nerve/ PHYSIOLOGY
SO - Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 1993;48(1):92-3
PY - 3
MMI concepts for 93230262 (3-pt AP=0.880795):
! 42.3 *Diaphragm
! 18.9 Phrenic Nerve
9.5 Fatigue
9.5 Shock
9.5 Pressure
6.5 Mouth
6.4 Lung
6.1 Relaxation
5.0 Social Change
4.9 Drive
4.5 Patients
OK:
An example with moderate 3-point average precision of 0.4867.
Citation:
UI - 93051935
AU - Vermerie N ; Kusielewicz D ; Tod M ; Nicolas P ; Perret G ; Fauvelle F ;
Petitjean O
TI - Pharmacokinetics of glafenine and glafenic acid in patients with cirrhosis,
compared to healthy volunteers.
AB - Pharmacokinetic parameters were evaluated in 12 patients with alcoholic
cirrhosis and 12 healthy volunteers after a single 400 mg oral dose of
glafenine. Glafenine (G) and its major active metabolite glafenic acid (GA)
were measured at regular intervals using a specific high performance liquid
chromatographic method. Glafenine absorption was significantly delayed in
cirrhotic patients (CP) (Tmax = 2.8 +/- 1.3 hvs 1.5 +/- 0.4 h, p less than
0.01) and was dramatically reduced in 3 patients. The large hepatic 'first
pass' effect observed in healthy volunteers was markedly reduced in CP
(ratio Cmax GA/Cmax G = 3.6 +/- 2.9 vs 18.9 +/- 9.8, p less than 0.001;
ratio areas under the curves AUC GA/AUC G = 2.3 +/- 2.3 vs 18.2 +/- 11.2,
p less than 0.001). The elimination half-life of G was prolonged in the CP
(13.0 +/- 13.1 h vs 1.5 +/- 0.5 h, p less than 0.01). In CP, GA elimination
half-life was increased (12.0 +/- 13.4 h vs 4.3 +/- 1.3 h, NS) but the
difference did not reach statistical significance because of large
variability. The significant rise of G plasma concentrations (Cmax = 2.2
+/- 2.1 mg/L vs 0.7 +/- 0.2 mg/L, p less than 0.05) and its longer
half-life would lead to an accumulation if the usual dosage regimen was
prescribed for CP and could result in nephrotoxicity. On the other hand,
lower dosage would be ineffective because only GA is active and
nephrotoxic. Hence, G should be given with great caution to CP.
MH - Administration, Oral; Adult ; Comparative Study ; Female ;
Glafenine/*ANALOGS & DERIVATIVES/ADMINISTRATION&
DOSAGE/*PHARMACOKINETICS ; Human ; Liver/METABOLISM ;
Liver Cirrhosis, Alcoholic/DRUG THERAPY/*METABOLISM ; Male ; Middle Age
SO - Fundam Clin Pharmacol 1992;6(4-5):197-203
PY - 2
MMI concepts for 93051935 (3-pt AP=0.486722):
! 59.0 *Glafenine
31.5 Pharmacokinetics
17.6 Voluntary Workers
17.5 Patients
13.7 Half-Life
13.0 Gases
! 10.9 *Liver Cirrhosis,
Alcoholic
6.6 Absorption
6.6 Hand
6.5 Plasma
6.5 Mouth
4.9 Lead
4.9 Methods
Poor:
An example with poor 3-point average precision of 0.2688.
Citation:
UI - 93287215
AU - Thali M ; Moore JP; Furman C ; Charles M ; Ho DD ; Robinson J ; Sodroski J
TI - Characterization of conserved human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120
neutralization epitopes exposed upon gp120-CD4 binding.
AB - Interaction with the CD4 receptor enhances the exposure on the human
immunodeficiency type 1 gp120 exterior envelope glycoprotein of conserved,
conformation-dependent epitopes recognized by the 17b and 48d neutralizing
monoclonal antibodies. The 17b and 48d antibodies compete with anti-CD4
binding antibodies such as 15e or 21h, which recognize discontinuous gp120
sequences near the CD4 binding region. To characterize the 17b and 48d
epitopes, a panel of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 mutants was
tested for recognition by these antibodies in the absence or presence of
soluble CD4. Single amino acid changes in five discontinuous, conserved,
and generally hydrophobic regions of the gp120 glycoprotein resulted in
decreased recognition and neutralization by the 17b and 48d antibodies.
Some of these regions overlap those previously shown to be important for
binding of the 15e and 21h antibodies or for CD4 binding. These results
suggest that discontinuous, conserved epitopes proximal to the binding
sites for both CD4 and anti-CD4 binding antibodies become better exposed
upon CD4 binding and can serve as targets for neutralizing antibodies.
MH - Amino Acid Sequence ; Animal ; Antibodies, Monoclonal/IMMUNOLOGY ;
Epitopes ; Antigens, CD4/*METABOLISM ; Cell Line ; Cercopithecus aethiops ;
Human ; HIV Antigens/*IMMUNOLOGY ; HIV Envelope Protein gp120/*IMMUNOLOGY ;
Macromolecular Systems ; Molecular Sequence Data ; Neutralization Tests ;
Protein Conformation ; Receptors, Virus/ *METABOLISM ;
Recombinant Proteins/IMMUNOLOGY ; Structure-Activity Relationship ;
Support, Non-U.S. Gov't ; Support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.
SO - J Virol 1993 Jul;67(7):3978-88
PY - 2
MMI concepts for 93287215 (3-pt AP=0.268771):
67.3 HIV-1
! 34.0 Epitopes
19.5 Antibodies
12.8 Antibodies, Anti-Idiotypic
12.7 Glycoproteins
! 11.5 *Antigens, CD4
8.1 Rabies
! 7.7 Antibodies, Monoclonal
6.6 Molecular Conformation
6.1 Binding Sites
5.0 Personality Tests
5.0 Social Change
3.4 Immunologic Deficiency Syndromes
3.3 Amino Acids
The Worst:
An example with universally bad precision of 0.0. The 3-point average is, of course, also 0.0.
Citation:
UI - 93020241
AU - Li WS ; McChesney JD
TI - Preparation of potential anti-inflammatory agents from dehydroabietic acid.
AB - Methyl 16-nor-16-carboxydehydroabietate (22),
16-nor-16-carboxydehydroabietinol acetate (23), methyl 7-keto-16-nor-16-
carboxydehydroabietate (29), 16-nor-16-carboxydehydroabietic acid (30),
16-nor-16-carboxydehydroabietinol (31), 7-keto-16-nor-16-
carboxydehydroabietic acid (32), methyl 7-hydroxy-16-nor-16-
carboxydehydroabietate (33), and 7-hydroxy-16-nor-16-carboxydehydroabietic
acid (34) were prepared from dehydroabietic acid. Only 22 and 32 had weak
anti-inflammatory activity.
MH - Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/CHEMISTRY/*ISOLATION &
PURIFICATION ; Diterpenes/*ANALYSIS
SO - J Pharm Sci 1992 Jul;81(7):646-51
PY - 2
MMI concepts for 93020241 (3-pt AP=0.000000):
17.7 Anti-Inflammatory Agents
9.1 Acids
8.2 Acetates